This post is also available in:
Español
Português
A refractometer is an optical instrument that measures the sucrose concentration of a solution based on the refractive index produced by light in that solution.

If we prepared several containers with different sugar-water solutions and placed a pencil in them, we would see how the pencil appears to bend more in those with a higher sugar concentration.
What the refractometer does is use a sample (in the case of beer, a wort sample) to project the curve produced by light onto a reticle containing a scale, allowing us to determine the angle formed by the light.
This value is represented in degrees Brix and indicates the percentage of sucrose present in the sample.
Contenido
Brix Refractometer
In summary, Brix degrees are a unit of quantity (°Bx) and are used to determine the total ratio of dry matter (usually sugars) dissolved in a liquid.
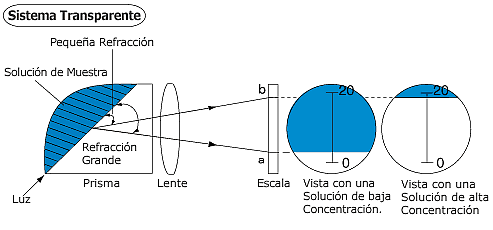
Technically, the refractive index (RI) is the ratio between the speed of light in a vacuum and the speed of light in the sample.
This is equal to the sine of the angle of incidence (I), or the angle at which light enters the water, divided by the sine of the angle of refraction (R), the degree to which the light appears to bend.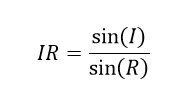
A refractometer looks like a small telescope. It has a window that we lift to place the sample (1 or 2 drops) and wait about 30 seconds to allow the sample to thermally stabilize and spread evenly.
The result, which is in degrees Brix, can be approximately converted to specific gravity using the following equation: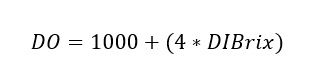
Where:
- DO: Is the original or initial density, read as we usually do.
- DIBrix: Is the initial density reading in degrees Brix obtained from the refractometer.
For example: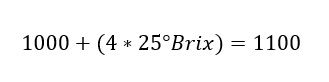
Some simply multiply the refractometer reading by 4 to get the specific gravity. For example, a reading of 11° Brix multiplied by 4 gives a specific gravity.
For example:
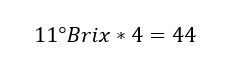
Que corresponde a una densidad de 1044.
A slightly more accurate formula would be:
Using this formula, a reading of 11° Brix results in a specific gravity of 1.043.
What Type of Refractometer Do You Need?
We can find a wide variety of refractometers, but homebrewers generally use those designed to measure fructose.
These have a range of 0-30° Brix (1.000-1.120), which is more than sufficient for our purposes, and also include automatic temperature compensation (ATC).
How to Use a Refractometer?
Before using a refractometer, the first thing we need to ensure is that it is calibrated. To do this, place a few drops of distilled water on the glass, close the lid, and make sure there are no empty spaces or air bubbles in the sample. Wait 30 seconds, hold the refractometer pointing it towards a light source, and look through the lens/eyepiece.
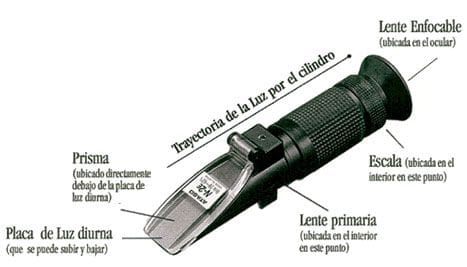
You will notice a blue and a white part. The horizontal line separating the two fields should mark 0° Brix; if not, adjust the calibration using a screw designed for this purpose.
Once calibrated, clean the window and take another measurement to ensure it is properly calibrated.
Temperature Correction
If your model has automatic temperature compensation, simply taking the reading will suffice.
Otherwise, use a chart to find the temperature correction factor (similar to a hydrometer).
Calibration should be done at room temperature, usually 20°C (68°F); no correction factor should be applied.
| Wort Temperature (°C) | Correction (SG) |
| 10 | +0.006 |
| 12 | +0.005 |
| 14 | +0.004 |
| 16 | +0.002 |
| 18 | +0.001 |
| 20 | 0.000 |
| 22 | -0.001 |
| 24 | -0.002 |
| 26 | -0.003 |
| 28 | -0.004 |
| 30 | -0.005 |
How to Apply the Correction Factor?
- Measure the temperature of the wort or beer with a thermometer.
- Note the hydrometer reading (specific gravity or density).
- Find the correction in the table based on the temperature.
Apply the correction:
- If the temperature is above 20°C, subtract the correction.
- If the temperature is below 20°C, add the correction.
For example:
- Hydrometer reading: 1.050 SG
- Wort temperature: 26°C
- Correction (from the table): -0.003
1.050 (reading) – 0.003 (correction) = 1.047 corrected SG
How to Calibrate a Refractometer?
If we compare the reading of a wort sample taken with a hydrometer to the reading from a refractometer, we will see that they are different.
Refractometers measure the percentage of sugar in a sucrose solution. However, our wort is not just sugar and water, so we can apply a correction to get an accurate reading.

The correction factor varies for each brewer and each beer. For very dark or high-density worts, a different correction factor may be needed.
To determine this factor, follow this procedure: first, measure the density with the refractometer, then take a sample, cool it, and measure it with the hydrometer.
Now convert the hydrometer reading to degrees Brix using the following equation: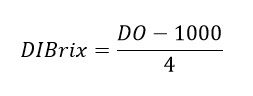
This DO is the original or initial density (DI) measured with the hydrometer. Then divide the refractometer reading by the hydrometer reading, which should give a result between 1.02 and 1.06.
Correction Factor
If you perform this check over several brews and average the results, you will obtain the correction factor needed for your beers.
Now that you have the correction factor, take the value from the refractometer and divide it by this number.
For example, if the reading is 14.6° Brix: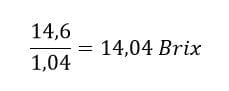
One thing to keep in mind is that refractometers have a margin of error of 0.2 to 0.3° Brix, so they are less precise than a good hydrometer.
However, the advantage of this method is the speed at which we can take readings of the wort at any point in the process.
For calculating the final density, the calculations are related to the initial density, meaning that even if the final readings are the same, the initial densities may differ.
Where:
- DF: Is the calculated final density.
- DFBrix: Is the refractometer reading after fermentation.
No se encontraron productos.
We recommend
- 5 Changes in Advertising and Beer Consumption in Chile
- Uses and Benefits of Beer for Hair: Everything You Need to Know